Allometric scaling of heat and water exchanges in the mammals' lung
Résumé
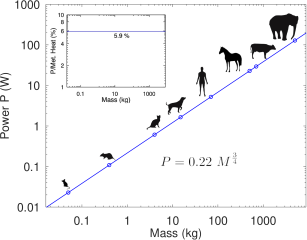
Heat exchanges in the mammals' lung are often considered negligible, despite of the lack of quantitive knowledge about their dynamics. Based on a modelling approach that allows to have both good quantitative predictions and full analytical solutions, we show that the heat exchanges are the consequence of a trade-off between the increase of the surface of the bronchi wall and the decrease of the driving gradients. This trade-off is driven by the temperature of the mucosa in the proximal bronchi that drives evaporation or condensation of the water in air. Although the resulting exchange patterns have a non trivial dependence on the mammals' mass, we show that the total amount of power dissipated in the lung obeys an allometric scaling law at rest. Strikingly, the system is driven by a single dimensionless number that is universal amongst mammals. In the ecological frame of the heat limitation dissipation theory, these exchanges bring a net evolutionary advantage from an organ designed for another function. We define the heat and water pulmonary diffusing capacities and derive their allometric scaling at rest. The heat diffusing capacity adapts to the animal so that the relative proportion of heat dissipated by its lung is independent on the animal's mass at rest, on the contrary of the proportion dissipated by the skin which decreases with the animal size. For human, our analysis also suggests that the heat and water diffusing capacities also adapt to the exercising level and keep up with the increase of heat production.
Fichier principal
 Fig_pannel3_bis_animals.pdf (761.79 Ko)
Télécharger le fichier
Fig_pannel1_tiers.pdf (2.04 Mo)
Télécharger le fichier
allometry_v2.1-arxiv.pdf (1.79 Mo)
Télécharger le fichier
humanExercise.pdf (2.66 Ko)
Télécharger le fichier
maxPowerLoc.pdf (454.39 Ko)
Télécharger le fichier
powerPerGens_animals.pdf (67.51 Ko)
Télécharger le fichier
Fig_pannel3_bis_animals.pdf (761.79 Ko)
Télécharger le fichier
Fig_pannel1_tiers.pdf (2.04 Mo)
Télécharger le fichier
allometry_v2.1-arxiv.pdf (1.79 Mo)
Télécharger le fichier
humanExercise.pdf (2.66 Ko)
Télécharger le fichier
maxPowerLoc.pdf (454.39 Ko)
Télécharger le fichier
powerPerGens_animals.pdf (67.51 Ko)
Télécharger le fichier
Origine : Fichiers produits par l'(les) auteur(s)
Origine : Fichiers produits par l'(les) auteur(s)

